
home contact company.overview news sitemap print
Contact |
|
Dr. Timm Danker |
|
 Isolated murine Langerhans islet (top) placed on a MEA chip (see below)
Isolated murine Langerhans islet (top) placed on a MEA chip (see below)
![]() Download Flyer
Download Flyer

Beta-cell Screen
to test drug effects on beta cell function in a Langerhans islet preparation
- Fast and reliable extracellular recording of beta-cell oscillatory activity with MEA-electrodes
- Determination of drug–induced effects on oszillatory activity of beta-cells presented as alteration in the Fraction of Plateau Phase (FOPP)
The assay is based on the recording of beta-cell oscillatory activity which is determined by the blood glucose concentration and in turn, regulates insulin secretion.
The membrane potential (Vm) of beta-cells oscillates at glucose concentrations between ~6 and 25 mM, i.e. burst phases with action potentials alternate with silent interburst phases generating so-called slow waves. The slow waves drive oscillations of the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]c) and insulin secretion. The length of the bursts correlates with the amount of insulin release. Thus, the fraction of plateau phase (FOPP), i.e. the percentage of time with burst activity, is an excellent marker for beta-cell function and metabolic integrity and can be used as ameasure to test for drug effects on beta-cell function and insulin release.


Drug effect on beta cell oszillations Drug effect on beta cell oscillations

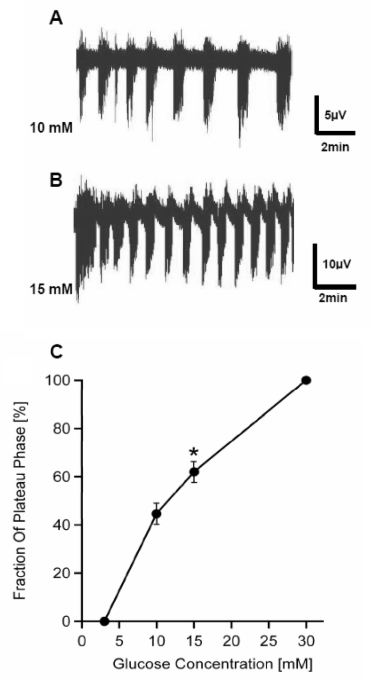
Glucose-dependent altration of beta-cell oszillatory activity (Pfeiffer et al. (2011) Glucose-dependent altration of beta-cell oszillatory activity
Publications:
Pfeiffer, T, Kraushaar U, Düfer M, Schönecker S, Haspel D, Guenther E, Drews G, Krippeit-Drews P. „Rapid functional evaluation of beta-cells by extracellular recording of membrane potential oscillations with microelectrode arrays“. Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology 462 (24. September 2011): 835–40. doi:10.1007/s00424-011-1029-z.
Schönecker S, Kraushaar U, Düfer M, Sahr A, Härdtner C, Guenther G, Walther R, et al „Long-Term Culture and Functionality of Pancreatic Islets Monitored Using Microelectrode Arrays“. Integrative Biology, Nr. 6 (24. März 2014): 540–44. doi:10.1039/C3IB40261D.
Schönecker, S, Kraushaar U, Guenther E, Gerst F, Ullrich S, Häring H-U,
Königsrainer A, Barthlen W, Drews G, und Krippeit-Drews P. „Human Islets
Exhibit Electrical Activity on Microelectrode Arrays (MEA)“.
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes: Official
Journal, German Society of Endocrinology [and] German Diabetes
Association, 8. April 2015. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1547217.

 +49 7121 51530 896
+49 7121 51530 896